イノベーション
市場からのさまざまな電気的および機械的要求をサポートするため、LEMは次のような様々な技術を開発しています。
- ホール効果オープンループ技術
- ホール効果クローズドループ技術
- 「ITタイプ」、「Cタイプ」、「CTSRタイプ」、「CAS-CASR-CKSRタイプ」、「ITCタイプ」などを含むフラックスゲート技術
- 「DVL&DVM&DVタイプ」を含むデジタル絶縁技術
- ロゴスキーコイル、PRiME™、電流トランスフォーマーなどのエアコア技術
ほとんどのアプリケーションでは、最適なソリューションは上記のいずれかの技術を使った標準トランスデューサであることがわかりますが、LEMはお客様独自の要求を満たすカスタマイズされたソリューションを開発することも可能です。
Hall Effect Current Sensors
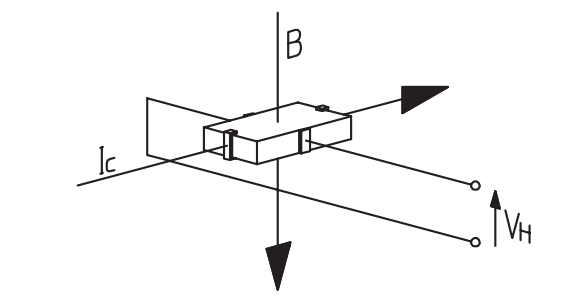
LEM Hall Effect current sensors are available in open-loop, closed-loop and Eta configurations.
Open-loop sensors are highly cost effective, as well as being small and consuming minimal power. Closed-loop sensors offer higher accuracy and enhanced speed to enable currents with a wider range of frequencies to be measured.
Hall Effect Eta transducers are similar in construction to closed loop sensors, with the same magnetic circuit geometry, a Hall generator and secondary winding. A Hall Effect Eta sensor is a mix of open loop and current transformer technologies operating as an open loop transducer at low frequencies (up to 2…10 kHz depending on the specific sensor design), and as a current transformer at higher frequencies. Both the Hall Effect and transformer signals are electronically added to form a common output signal.
FLUXGATE CURRENT SENSORS
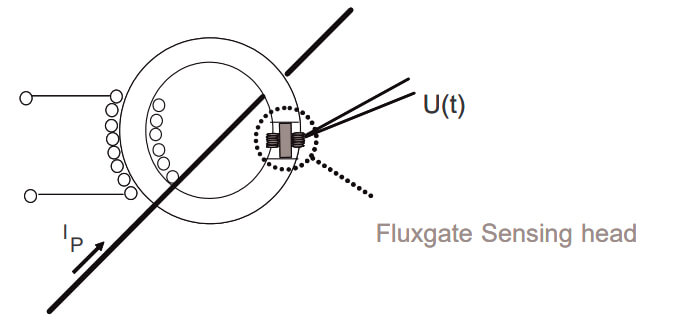
A “standard” closed-loop Fluxgate sensor uses a secondary winding to counteract the field generated in a magnetic circuit by the primary conductor. Although similar in operation to a closed-loop Hall Effect sensor, the Fluxgate uses a saturable inductor using a small thin magnetic core to sense the airgap field, rather than a Hall Effect sensor.
Other Fluxgate sensors built on the technology to deliver specific benefits. They are:
- Low-Frequency, where the field sensing element is wrapped around the toroidal core, rather than using a gap to make more cost-effective sensors
- C-Type, built like the low-frequency Fluxgate sensor, but with a separate core to improve high frequency performance
- IT-type that uses two toroidal cores with opposing excitation coils.
AIR-CORE CURRENT SENSORS
The material used to create the core can limit the performance of the sensor due to characteristics such as remanence, hysteresis, non-linearity, losses and saturation. So the design of an air-core or coreless sensor is often considered.
Examples of air-core current sensors include Rogowski coil sensors.
The Rogowski coil and PRiME™ technologies both work on the same basic principle; a pick-up coil is magnetically coupled with the flux created by the current to be measured. A voltage is induced on the pick-up coil proportional to the derivative of flux and thus proportional to the derivative of the current to be measured. Because the derivative of DC is zero these technologies are only useful for the measurement of AC or pulsed currents.
Insulating Digital Technology
Operation principle Insulating Digital Technology
The measuring voltage, VP, is applied directly to the voltage sensor primary connections through a resistor network allowing the signal conditioning circuitry to feed a Sigma-Delta modulator that allows to transmit data via one single isolated channel.
The signal is then transmitted to the secondary over an insulating transformer ensuring the insulation between the high voltage side (primary) and the low voltage side (secondary).
The signal is reshaped on the secondary side, then decoded and filtered through a digital filter to feed a micro-controller using a Digital/Analog (D/A) converter and a voltage to current generator.
The recovered output signal is completely insulated against the primary and is an exact representation of the primary voltage.
Main features
- Measurement of all types of signals: DC, AC, pulsed and complex
- Low volume technology: compact size
- High galvanic insulation between primary (high power) and secondary circuits (electronic circuit)
- Low consumption technology
- Very high accuracy
- Low temperature drift